How to operate a drone? It’s a question sparking curiosity in many. This guide unravels the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding the basic components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight techniques and ensuring safe operation. We’ll explore various drone types, control mechanisms, camera functionalities, and essential safety regulations, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
We’ll cover everything from basic maneuvers like takeoff and landing to more advanced techniques such as waypoint navigation. Safety is paramount, and we’ll delve into crucial safety protocols and regulatory considerations to ensure responsible and enjoyable drone piloting.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the function of each major part and explores the differences between various drone types.
Drone Component Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated operation of several key components. These include:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust necessary for flight, maneuvering, and stability. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical rotation. Brushless motors are commonly used for their efficiency and durability.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, the flight controller processes data from various sensors and controls the motors to maintain stability and execute flight commands. It’s a miniature computer managing the entire flight system.
- Battery: Provides the power source for the motors and other electronic components. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are prevalent due to their high energy density and lightweight nature.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): Allows the drone to determine its location and maintain a stable position in the air, crucial for autonomous flight and features like “Return to Home”.
- Camera: Captures images and videos, a primary function for many drone users. Camera quality varies significantly across different drone models.
Drone Type Differences
Drones are categorized by their number of rotors, each impacting flight characteristics and stability:
- Quadcopter (4 rotors): The most common type, offering a good balance of maneuverability and stability. Relatively simple to operate and widely available.
- Hexacopter (6 rotors): Offers increased redundancy and stability compared to quadcopters, making them suitable for heavier payloads or challenging weather conditions. More complex to control.
- Octocopter (8 rotors): Provides exceptional stability and redundancy, ideal for professional applications requiring heavy payloads or extended flight times. More expensive and requires greater piloting skill.
Popular Drone Model Comparison
The following table compares the specifications and capabilities of three popular drone models (Note: Specifications are illustrative and may vary based on model year and specific configuration):
| Feature | Drone Model A | Drone Model B | Drone Model C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Flight Time | 30 minutes | 25 minutes | 40 minutes |
| Camera Resolution | 4K | 1080p | 4K |
| Max Payload | 0.5 kg | 0.25 kg | 1 kg |
| GPS | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This section Artikels the necessary steps and best practices.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously follow this checklist:
- Inspect propellers for damage or debris.
- Check motor functionality and responsiveness.
- Verify battery charge level and health.
- Ensure GPS signal is strong and accurate.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Confirm camera settings and functionality.
- Review local airspace regulations and restrictions.
- Check weather conditions (wind speed, visibility).
Sensor and Compass Calibration
Proper calibration of the drone’s sensors is crucial for accurate flight. This typically involves performing a level calibration and compass calibration using the drone’s software or app. Refer to your drone’s manual for specific instructions. These steps help ensure accurate readings and prevent erratic flight behavior.
Pre-Flight Preparation Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight process can enhance efficiency and reduce the likelihood of overlooking critical steps. The flowchart would begin with “Power On,” branch to “Propeller Inspection,” “Battery Check,” “GPS Acquisition,” and “Sensor Calibration,” converging at “Flight Ready.”
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are fundamental to responsible drone operation. This section details proper techniques and emergency protocols.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Techniques
A smooth takeoff involves gently increasing throttle until the drone lifts off vertically. Maintain a steady ascent, avoiding abrupt movements. Landing should be performed gradually, reducing throttle to a gentle descent. Avoid sudden drops or jerky maneuvers. Always land in a clear, open area free from obstacles.
Handling Wind Conditions
Wind significantly affects drone stability. In windy conditions, perform takeoffs and landings into the wind to minimize drift. Reduce speed and be prepared for adjustments to maintain control. Strong winds may necessitate postponing the flight altogether.
Emergency Landing Procedure
In case of loss of signal, malfunction, or other emergencies, initiate an immediate descent. If possible, utilize the “Return to Home” (RTH) function. If RTH is unavailable, gently lower the drone to the ground, prioritizing a safe landing over preserving the drone’s condition.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all these elements, including safety procedures and legal considerations, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. This will help ensure you operate your drone safely and responsibly.
Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding the drone controller and available flight modes is essential for effective navigation. This section details controller functions and flight mode applications.
Drone Controller Functions
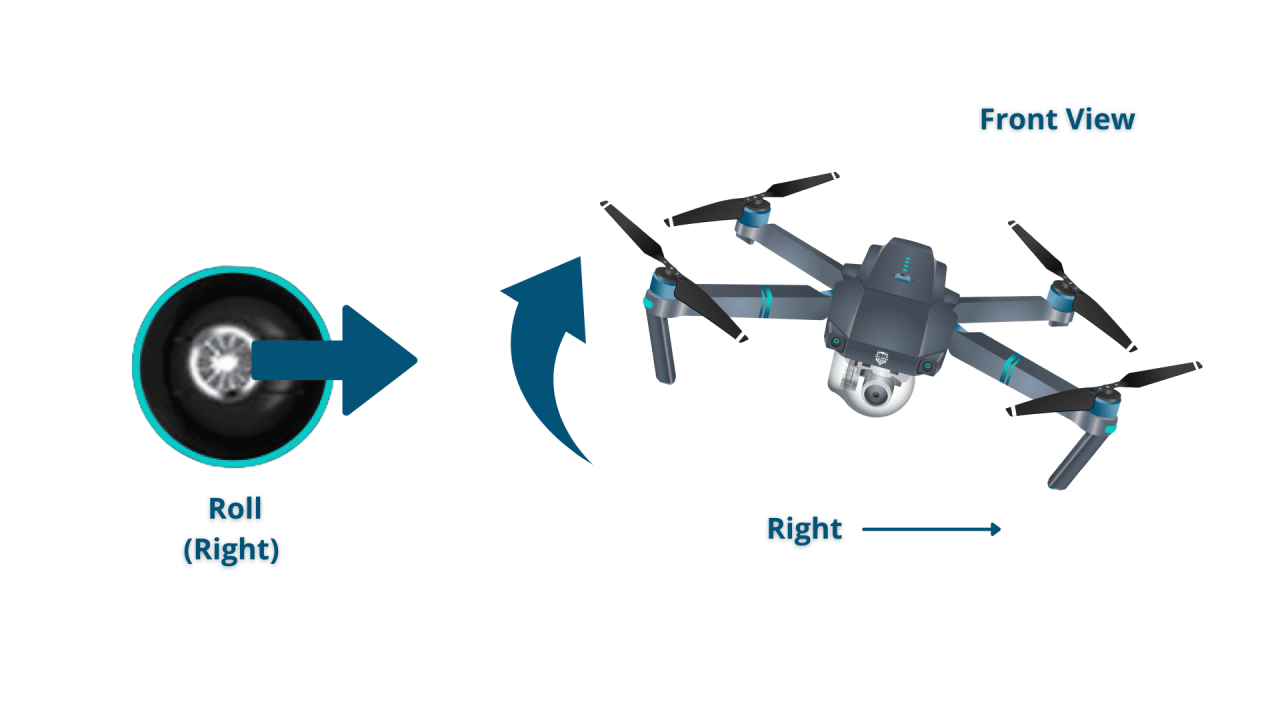
Standard drone controllers typically feature two joysticks. The left joystick controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right joystick controls pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right). Buttons on the controller activate functions like camera control, return-to-home, and flight mode selection.
Common Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of autonomy and control:
- GPS Mode: The drone maintains its position using GPS data, making it easier to hover and perform precise movements.
- Attitude Mode: The drone responds directly to joystick inputs, disregarding GPS data. This provides greater maneuverability but requires more skill to maintain stability.
- Manual Mode: Offers full manual control with minimal stabilization assistance. Requires significant piloting experience and is generally not recommended for beginners.
GPS vs. Manual Control
The choice between GPS and manual control depends on the flight situation and pilot experience. GPS mode offers stability and ease of use, ideal for beginners and tasks requiring precision. Manual mode offers greater maneuverability but demands higher skill levels and is best suited for experienced pilots in controlled environments.
Flight Techniques and Maneuvers
Mastering basic and advanced flight maneuvers enhances drone control and expands operational capabilities. This section explores essential techniques for smooth and controlled flight.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Basic maneuvers include hovering (maintaining a fixed position), ascending (increasing altitude), descending (decreasing altitude), and turning (rotating the drone). Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area to build confidence and control.
Flying in Confined Spaces
Flying in confined spaces requires increased precision and awareness. Maintain slow speeds and use small, deliberate movements. Always be aware of obstacles and maintain a safe distance.
Achieving Smooth and Controlled Flight
Smooth and controlled flight is achieved through practice and deliberate control inputs. Avoid jerky movements and maintain consistent throttle and stick inputs. Familiarize yourself with your drone’s response characteristics and adjust your piloting technique accordingly.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
The camera is a key feature of many drones. Understanding camera settings and techniques allows for optimal image capture. This section details camera operation and settings for various photography types.
Setting Up Drone Camera Settings
Camera settings like resolution, frame rate, and exposure impact image quality. Higher resolution and frame rates result in sharper images and smoother videos but require more storage space. Exposure settings control brightness and contrast, adjusting according to lighting conditions.
Camera Angles and Perspectives
Drones offer unique perspectives unattainable with traditional cameras. Experiment with different angles, such as bird’s-eye views, low-angle shots, and dynamic tracking shots to enhance creativity and storytelling.
Camera Settings for Aerial Photography
Optimal camera settings vary based on the type of aerial photography:
| Photography Type | Resolution | Frame Rate | Exposure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landscape | 4K | 24fps | Balanced |
| Portrait | 4K | 24fps | Slightly overexposed |
| Action Shots | 1080p | 60fps | Fast shutter speed |
Drone Safety and Regulations
Safe and responsible drone operation requires adherence to regulations and safety guidelines. This section emphasizes the importance of respecting airspace and prioritizing safety.
Airspace Regulations and Permits
Before flying, research and understand local airspace regulations. Many countries and regions require registration and permits for drone operation, especially near airports, restricted areas, or for commercial purposes. Failure to comply can result in penalties.
Safety Measures to Avoid Accidents, How to operate a drone
Always maintain visual line of sight with the drone. Avoid flying in inclement weather or near obstacles. Never fly over crowds or sensitive areas. Regularly inspect the drone for damage and ensure batteries are properly charged and stored.
Safe Drone Operation Practices Poster
A visual poster would depict key safety practices, including maintaining visual line of sight, checking weather conditions, respecting airspace restrictions, and keeping a safe distance from obstacles and people. The poster would also include emergency contact information.
Battery Management and Charging
Proper battery care is essential for maximizing drone performance and lifespan. This section details safe charging and storage practices.
Importance of Proper Battery Care
LiPo batteries require careful handling. Overcharging, discharging too deeply, or exposing them to extreme temperatures can damage the battery and pose a safety risk. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for charging and storage.
Safe Charging and Storage
Use only the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow the charging instructions precisely. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials. Never leave charging batteries unattended.
Maximizing Battery Life and Performance
Avoid completely depleting the battery. Store batteries at a partially charged state (around 30-50%). Avoid extreme temperatures and maintain the battery’s connections clean.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Addressing common drone malfunctions efficiently minimizes downtime and ensures continued operation. This section provides troubleshooting steps for common problems.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common issues include loss of signal (due to distance, interference, or battery issues), motor failure (due to damage or low voltage), and GPS issues (due to signal blockage or interference). Other problems can stem from faulty sensors or software glitches.
Troubleshooting Steps for Common Problems
Troubleshooting steps vary depending on the specific issue. For loss of signal, try moving closer to the drone or restarting the controller. For motor failure, check for physical damage and ensure sufficient battery power. For GPS issues, ensure a clear view of the sky and try recalibrating the GPS.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
A flowchart would guide users through a series of diagnostic steps based on the reported problem. The flowchart would branch based on the symptoms, ultimately leading to potential solutions or recommending contacting support.
Advanced Drone Techniques

Advanced techniques unlock greater operational capabilities and expand the applications of drone technology. This section explores waypoint navigation and autonomous flight.
Waypoint Navigation and Autonomous Flight
Waypoint navigation allows the drone to follow a pre-programmed path, automatically navigating between specified points. Autonomous flight encompasses more advanced features, such as object avoidance and automated mission execution. These features are often controlled through specialized software.
Use of Drone Software for Flight Planning
Drone software enables detailed flight planning, including setting waypoints, defining flight parameters, and controlling camera settings. This allows for more complex and efficient missions.
Drone Flight Planning Software Options

Various software options are available, each offering a range of features and capabilities. Some popular choices include [Software A], [Software B], and [Software C], each with varying levels of complexity and pricing.
Mastering drone operation is a journey of learning and practice. By understanding the fundamental components, mastering flight controls, adhering to safety regulations, and continually refining your skills, you’ll unlock the potential of aerial exploration. Remember, responsible operation is key to ensuring both your safety and the safety of others. So, embrace the challenge, and enjoy the exciting world of drone piloting!
Questions and Answers: How To Operate A Drone
What is the minimum age requirement to operate a drone?
Age restrictions vary depending on the country and drone regulations. Check your local laws for specific age limits.
Learning to operate a drone safely and effectively involves understanding its controls and capabilities. A crucial first step is familiarizing yourself with the basics, which can be easily done by checking out comprehensive guides like this one on how to operate a drone. From there, practice is key to mastering flight maneuvers and ensuring you’re comfortable handling your drone in various conditions.
Remember to always prioritize safety when operating a drone.
How far can I fly my drone?
The maximum distance depends on the drone’s capabilities and regulatory limitations. Always stay within the legal flight range and maintain visual line of sight.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this if possible. If not, try to regain signal or perform an emergency landing.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements differ based on location. Consult your local aviation authority for specific registration procedures and requirements.
